The Heart of a Human: A Marvel of Life

The Heart of a Human: A Marvel of Life
The human heart, often romanticized in poetry and literature as the seat of emotions, is much more than a symbol of love. It is a muscular, tireless organ responsible for keeping us alive, beating approximately 100,000 times a day and pumping about 2,000 gallons of blood. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this incredible organ and its vital role in our existence.
The Anatomy of the Heart
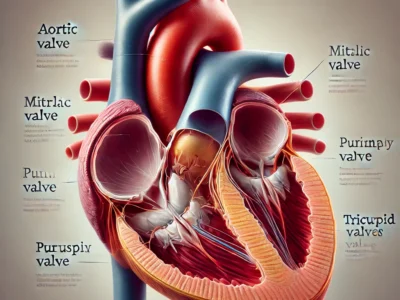
The heart is situated slightly to the left of the chest, shielded by the ribcage. It is divided into four chambers:
- The right atrium and right ventricle, which pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
- The left atrium and left ventricle, which pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
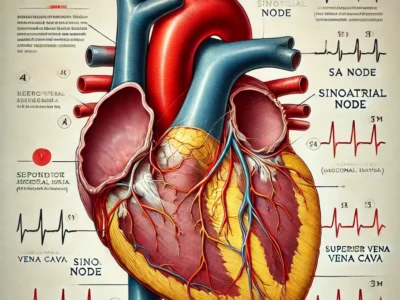
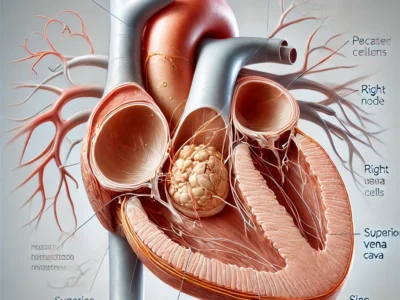
These chambers work in a rhythmic harmony, driven by electrical impulses generated by the sinoatrial node, often called the heart’s natural pacemaker. The valves in the heart ensure that blood flows in one direction, preventing backflow and maintaining efficiency.
The Function of the Heart
At its core, the heart is a pump that circulates blood through two main pathways:
- Pulmonary Circulation: The right side of the heart sends blood to the lungs to receive oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide.
- Systemic Circulation: The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to tissues.
This circulation is critical for survival, as it supports cellular function, removes waste products, and helps regulate body temperature.
The Heart and Health
The heart is resilient, but like any organ, it is susceptible to wear and disease. Cardiovascular diseases are among the leading causes of death worldwide, often attributed to factors like unhealthy diets, lack of exercise, smoking, and stress. Common heart conditions include:
- Coronary artery disease: Blockage of blood vessels supplying the heart.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats due to electrical malfunctions.
- Heart failure: The heart’s inability to pump blood effectively.
Preventing heart disease involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle: regular physical activity, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, avoiding tobacco, and managing stress.
The Emotional Connection
While the brain controls emotions, the heart often reflects them physically. Fear, excitement, and love can all increase heart rate, highlighting the deep connection between our physical and emotional states. This link between the heart and emotions has cemented its place as a symbol of human passion and vitality throughout history.
The Heart in Modern Medicine
Advancements in medicine have greatly improved our understanding and treatment of heart conditions. Procedures like angioplasty, heart transplants, and artificial pacemakers have saved countless lives. Innovations in wearable technology now allow people to monitor their heart health in real-time, providing early warnings for potential issues.
Conclusion
The human heart is more than an organ; it is a symbol of life and resilience. By taking care of our hearts, we not only extend our lives but also improve our quality of life. So, let’s treat this incredible engine with the respect and care it deserves—after all, it works tirelessly for us every moment of every day.
Let your heart inspire you to live vibrantly and love wholeheartedly!
- What is Pulmonary artery?
- Function of Pulmonary artery?
- What will happen if pulmonary artery don’t work ?
- How many valve are in heart ?
- The Anatomy of the Human Heart: A Guide to Its Structure and Function?
- How the Heart Works: Understanding Blood Circulation in the Body?
- Heart Health: Tips for Maintaining a Strong and Healthy Heart ?
- The Role of Diet in Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
- How Exercise Benefits the Heart and Improves Circulation