Function of Pulmonary artery
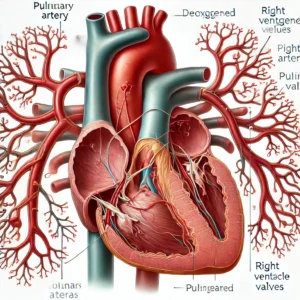
The pulmonary artery plays a crucial role in the circulatory system. Its primary function is to transport deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its function:
Key Functions of the Pulmonary Artery:
1. Transport of Deoxygenated Blood:
- The pulmonary artery carries blood low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide from the right ventricle to the lungs.
2. Facilitation of Gas Exchange:
- Once in the lungs, the blood is enriched with oxygen and releases carbon dioxide through a process called gas exchange in the alveoli (tiny air sacs).
3. Separation of Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation:
- The pulmonary artery ensures that the blood destined for oxygenation is directed to the lungs, maintaining the distinction between pulmonary (lungs) and systemic (body) circulatory pathways.
4. Support for Efficient Oxygenation:
- By delivering blood to the lungs, the pulmonary artery helps maintain the body’s oxygen supply, which is critical for cellular respiration and energy production.
5. Regulation of Blood Pressure in Pulmonary Circulation:
- The pulmonary artery works under lower pressure compared to systemic arteries, preventing strain on the delicate lung tissues.
Significance in Health and Disease:
- Proper functioning of the pulmonary artery is essential for maintaining normal oxygen levels in the blood.
- Conditions like pulmonary hypertension or pulmonary embolism (blockage in the pulmonary artery) can disrupt its function, leading to serious health complications.
In essence, the pulmonary artery serves as the vital link between the heart and the lungs, ensuring that blood is oxygenated before being distributed to the rest of the body.
What's your reaction?
Excited
0
Happy
0
In Love
0
Not Sure
0
Silly
0







